| SODIUM CYCLAMATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 139-05-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 205-348-9 | |
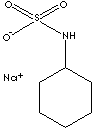
| FORMULA | C6H11NHSO3Na | |
| MOL WT. | 201.22 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2921.30.5000 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral Rat LD50: 1280mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Sodium cyclohexanesulfamate; | |
| Cyclohexanesulfamic acid monosodium salt; Assugrin; Asugryn; Cyclohexylsulfamic acid monosodium salt; Hachi-sugar; Ibiosuc; Sodium cyclohexyl amidosulfate; Sodium cyclohexyl sulfamate; Sodium cyclohexylsulfamidate; Sodium N-cyclohexylsulfamate; N-Cyclohexylsulphamic acid sodium salt; Sodium sucaryl; Suessette; Suestamin; N-Cyklohexylsulfamat sodny; Natraiumcyclohexylamidosulfat; Other RN: 53170-91-5, 61373-78-2 | ||
| SMILES | C1(NS(=O)(=O)[O-])CCCCC1.[Na+] | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Sweetener, Sulfamate |
|
|
EXTRA NOTES |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white crystals | |
| MELTING POINT | >300 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
200 g/l |
|
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
Insoluble in ether and benzene | |
| pH | 5.5 - 7.0 | |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1 ; Flammability: 0 ; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
FLASH POINT |
> 200 C |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. | |
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||
|
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Sodium cyclamate PubChem Compound Summary - Sodium cyclamate IPCS INCHEM - Sodium cyclamate KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Sodium cyclamate http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Sodium cyclamate http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Sodium cyclamate Human Metabolome Database - Sodium cyclamate http://journals.sfu.ca/ Sweeteners permitted in the European Union: safety aspects Cyclamate (E952): Three different compounds are referred to as cyclamates: cyclamic acid, calcium cyclamate and sodium cyclamate. Cyclamates, whether in the form of sodium cyclamate or calcium cyclamate, are stable in heat and cold and have good shelf-life. The stability and solubility in water facilitate the use of cyclamates in foodstuffs and beverages. Cyclamate has the lowest sweetening power of the intense sweeteners, but combined with other intense sweeteners, a synergistic effect masks the aftertaste associated with the use of a single sweetener. The mixture of 10 parts cyclamate and one part of saccharin was widely used in foods and beverages during the 1960s. In 1969, however, cyclamate was prohibited in many countries because bladder tumours were found in rats fed with the 10:1 cyclamate saccharin mixture (33). Since then, several additional toxicity and carcinogenicity studies have been conducted with cyclamate, the cyclamate saccharin mixture and cyclamate meta- Safety aspects of sweeteners metabolite cyclohexylamine (CHA). Local: |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION (NF-13, BP93) | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystals | |
|
ASSAY |
98.5% - 101.0% |
|
|
pH |
5.5 - 7.0 |
|
|
FREE ACID |
0.3% max |
|
|
SULFATE |
0.1% max |
|
|
CYCLOHEXYLAMINE |
1ppm max |
|
|
DICYCLOHEXYLAMINE |
10ppm max |
|
|
ANILINE |
1ppm max |
|
|
As |
3ppm max |
|
|
Pb |
1ppm max |
|
|
Se |
30ppm max |
|
|
HEAVY MERALS |
10ppm max |
|
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
0.5% max |
|
| ABSORPTION |
0.1 max (270nm) |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. |
Not Regulated. |
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
Harmful if swallowed. May cause eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. OSHA Hazards:Target Organ Effect, Harmful by ingestion. Target Organs: Liver, Kidney, Bladder, Pancreas., Testes., Cardiovascular system. |
|
|
GHS |
|
|
| SIGNAL WORD | Warning | |
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H302 |
|
|
P STATEMENTS |
P301+ P312 | |
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
22 |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
24/25-45 |
|
| PRICE INFORMATION | ||
|
|
||